
The lipid molecules are attached to the carbohydrates by the glycosidic bond.Ģ. There are some interesting features of this lipid molecule.ġ. It is an important class of cell membrane lipids that are synthesized by both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. It acts as a receptor for bacterial protein toxins, such as cholera toxins and pituitary glycoprotein hormones (4) & (5). The Ganglioside is the primary component of an animal’s cell membrane. Gangliosides are also found in red blood cells and parenchymatous tissues, like spleen tissue. The amount of sialic acid is very high in this type of glycolipid. Gangliosides are composed of sialic acid (sugar) and ceramide (fatty acid). It is found in ganglion cells of nervous tissue. Its primary function is to protect the nerve cells. They are also found in the myelin sheath of the nerve system. It is known as galactolipids because it is composed of galactose. Phosphoric acid groups are not present in these types of glycolipids. Cerebrosides are found in large amounts in the brain. They are composed of fatty acid, sphingosine, and galactose. These lipid molecules are found in large amounts in the brain and myelin sheaths of nerves. It contains fatty acids, amino alcohol sphingosine, and carbohydrate molecules. These molecules interact with each other, especially in animal cells, through hydrogen bonds between their carbohydrate chain and by van der wales forces within their fatty acid chains (4) & (7). It is found in unicellular organisms such as bacteria and yeast, as well as in complex organisms such as animals and plants. Chloroplast membranes of plant cells contain high levels of these lipid molecules.
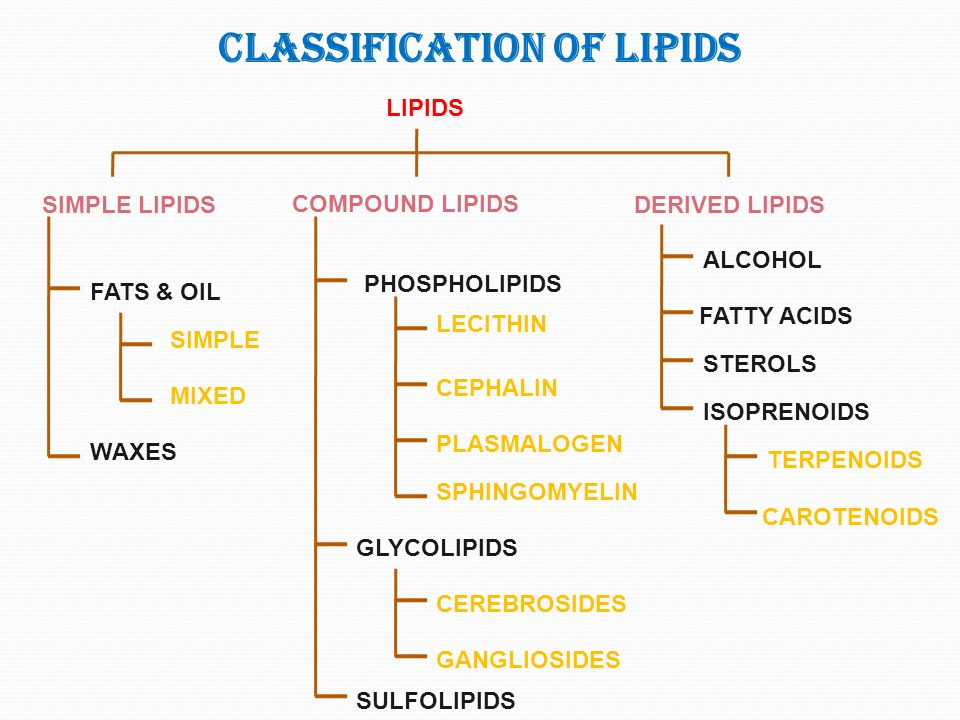
When galactose is attached to a lipid, it is called a galactolipid. In this case, glucose or galactose is attached with lipids. It contains nitrogen but and no phosphoric acid. It is a compound lipid that is when carbohydrates are combined with simple lipids (fatty acids), forms a glycolipid. Below is a description of its structure and how it works (3) & (6). It is a very important lipid of the cell membrane. On the outside of this phospholipid layer, there is often a tiny carbohydrate chain attached called glycolipids. Protein molecules are scattered in the phospholipid layer.

The cell membrane is usually composed of phospholipid bilayers. All eukaryotic cells contain these molecules on the membrane surface.

They play an important role in the photosynthesis process. The main function of lipids is to store energy and act as components of cell membrane formation.Īccording to the structure, there are three types of lipids, simple, compound, and derivative lipids. Lipids are an important biochemical compound in plants and animals, consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Only 5% of lipids in the cell membrane are glycolipids. Glycolipids are the component of the cell membrane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
